Development-Disability
Development-Disability
Most common developmental disabilities:
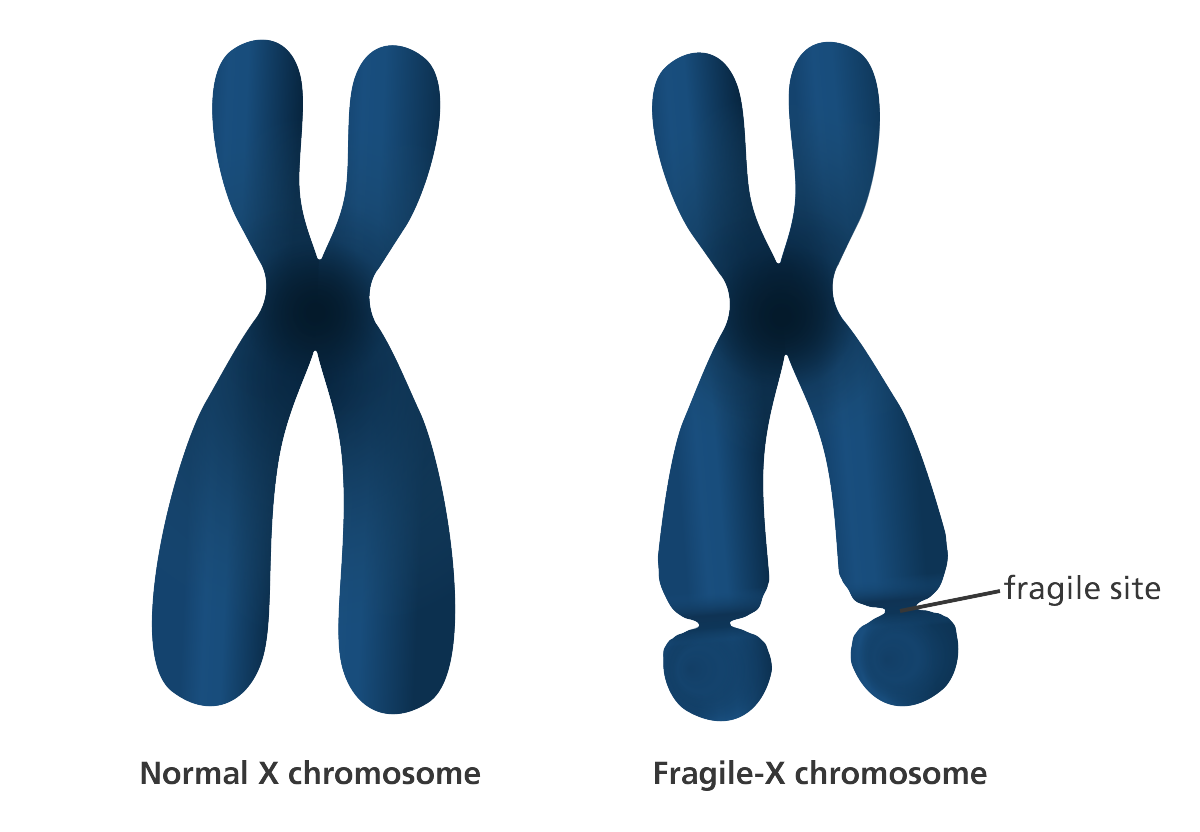
- Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is thought to cause autism and intellectual disability, usually among boys.
- Down syndrome is a condition in which people are born with an extra copy of chromosome 21. Normally, a person is born with two copies of chromosome 21. However, if they are born with Down syndrome, they have an extra copy of this chromosome. This extra copy affects the development of the body and brain, causing physical and mental challenges for the individual.
- Pervasive developmental disorders (PDD) are a group of developmental disabilities that can cause significant social, communication and behavioral challenges.
- Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) are a group of conditions that can occur in a person whose mother drank alcohol during pregnancy. FASDs are 100% preventable if a woman does not drink alcohol during pregnancy.
- Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that affect a person’s ability to move and maintain balance and posture. CP is the most common motor disability in childhood.
- Intellectual disability, also (sometimes proscriptively) known as mental retardation, is defined as an IQ below 70 along with limitations in adaptive functioning and onset before the age of 18 years.
Challenging behaviour
Some people with developmental disabilities exhibit challenging behavior, defined as "culturally abnormal behaviour(s) of such intensity, frequency or duration that the physical safety of the person or others is placed in serious jeopardy, or behaviour which is likely to seriously limit or deny access to the use of ordinary community facilities. Common types of challenging behavior include self-injurious behavior (such as hitting, head butting, biting), aggressive behavior (such as hitting others, screaming, spitting, kicking, swearing, hairpulling), inappropriate sexualized behavior (such as public masturbation or groping), behavior directed at property (such as throwing objects and stealing) and stereotyped behaviors (such as repetitive rocking, echolalia or elective incontinence). Such behaviors can be assessed to suggest areas of further improvement, using assessment tools such as the Nisonger Child Behavior Rating Form (NCBRF).
Challenging behavior in people with developmental disabilities may be caused by a number of factors, including biological (pain, medication, the need for sensory stimulation), social (boredom, seeking social interaction, the need for an element of control, lack of knowledge of community norms, insensitivity of staff and services to the person's wishes and needs), environmental (physical aspects such as noise and lighting, or gaining access to preferred objects or activities), psychological (feeling excluded, lonely, devalued, labelled, disempowered, living up to people's negative expectations) or simply a means of communication. A lot of the time, challenging behavior is learned and brings rewards and it is very often possible to teach people new behaviors to achieve the same aims. Challenging behavior in people with developmental disabilities can often associated with specific mental health problems.
Speech Delay
From 18 to 24 Months. Though there is a lot of variability, most toddlers are saying about 20 words by 18 months and 50 or more words by the time they turn 2. By age 2, kids are starting to combine two words to make simple sentences, such as "baby crying" or "Daddy big."
Developmental speech and language disorder is a common reason for speech/language problems in kids. This is a learning disability that is caused by the brain working differently. These kids may have trouble producing speech sounds, using spoken language to communicate, or understanding what other people say.
Acquired neurological communication disorders are language and communication difficulties/disorders due to an aquired brain disorder. An acquired brain disorder(ABD) is defined as a disruption in brain functioning that:anoxic or hypoxic injury to the brain such as cardio pulmonary arrest or carbon.
Mixed receptive-expressive language disorder is diagnosed when a child has problems expressing him-or herself using spoken language, and also has problems understanding what people say to him or her.
Here are some simple ways to nurture your baby's language development.
- Talk, talk, talk
- Read, read, read
- Enjoy music together
- Tell stories
- Follow your child's lead
- Never criticize your child's articulation or speech patterns
- Use television and computers sparingly
- Treat ear infections thoroughly
Disability Benefits for Learning Disabilities. Children with a developmental delay established by psychological or neuro psychological tests to be related to an organic factor in the brain may be able to get disability benefits if they have severe impairment in two of the following areas: cognitive/communicative ...
Difficulties pronouncing sounds, or articulation disorders, and stuttering are examples of speech disorders. When a person has trouble understanding others (receptive language), or sharing thoughts, ideas, and feelings completely (expressive language), then he or she has a language disorder.
Expressive language disorder is a communication disorder in which there are difficulties with verbal and written expression. Expressive language disorder affects work and schooling in many ways. It is usually treated by specific speech therapy, and usually cannot be expected to go away on its own.
Some mixed language disorders are caused by a brain injury. These conditions are sometimes mis diagnosed as developmental disorders. Language disorders may occur in children with other developmental problems, autism spectrum disorder,hearing loss, and learning disabilities.
A child with receptive language disorder has difficulties with understanding what is said to them. The symptoms vary between children but, generally, problems with language comprehension begin before the age of three years. Children need to understand spoken language before they can use language to express themselves.
So here are our top seven strategies for promoting language development in nonverbal children and adolescents with autism:
- Encourage play and social interaction
- Imitate your child
- Focus on nonverbal communication
- Leave “space” for your child to talk
- Simplify your language
- Follow your child's interests
'Disability' test is not difficult to meet. It is reasonably easy for a stammer to come within the Equality Act. Broadly, a stammer is covered if it has a substantial adverse effect on one's ability to carry out normal day-to-day activities, such as having a conversation or using the telephone.
In most cases, stuttering will be a disability. A disability is an impairment that significantly impacts a major life activity. The ADA includes “speaking” and “communication” as a major life activities. So, if the stutter significantly affects one's ability to communicate, it will be a disability.
Stuttering is a speech disorder in which sounds, syllables, or words are repeated or prolonged, disrupting the normal flow of speech. These speech disruptions may be accompanied by struggling behaviors, such as rapid eye blinks or tremors of the lips.
Behavioral disorders, also known as disruptive behavioral disorders, are the most common reasons that parents are told to take their kids for mental health assessments and treatment. If left untreated in childhood, these disorders can negatively affect a person's ability to hold a job and maintain relationships.
Behavioral disorders, also known as disruptive behavioral disorders, are the most common reasons that parents are told to take their kids for mental health assessments and treatment. Behavioral disorders are also common in adults.
EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIORAL DISORDER (EBD) An emotional and behavioral disorder is an emotional disability characterized by the following: An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships with peers and/or teachers.
Disruptive behavior disorders include two similar disorders: oppositional defiantdisorder (ODD) and conduct disorder (CD). Common symptoms occurring in children with these disorders include: defiance of authority figures, angry outbursts, and other antisocial behaviors such as lying and stealing.
Students with EBD that show externalizing behavior are often diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional defiant disorder(ODD), conduct disorder, and/or bipolar disorder; however, this population can also include typically developing children that have learned to exhibit externalizing.
Emotional and behavioral disorders (EBD; sometimes called emotional disturbance or serious emotional disturbance) refer to a disability classification used in educational settings that allows educational institutions to provide special education and related services to students that have poor social or academic
Developmental disorders is a group of psychiatric conditions originating in childhood that involve serious impairment in different areas. There are several ways of using this term.
40% of children with ADHD also develop oppositional defiant disorder, a condition marked by chronic aggression, frequent out bursts, and a tendency to argue, ignore requests, and engage in annoying behavior. Begin to understand your defiant child here.
It's normal for children to occasionally forget their homework, daydream during class, act without thinking, or get fidgety at the dinner table. But inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity are also signs of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD or ADD).
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) affects children and teens and can continue into adulthood. ADHD is the most commonly diagnosed mental disorder of children. Children with ADHD may be hyperactive and unable control their impulses. Or they may have trouble paying attention
“A significant 45 to 85 percent of kids with ADHD develop oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), averaging about 65 percent across studies,” Barkley said. Emotional out bursts and physical aggression are not easily controlled when a child has ODD, and this behavior can cause a lot of stress for families.
There is nothing a parent can do to cause ADHD. Children with ADHD benefit from structure and positive reinforcement, so pay attention to what your child is doing well. Rory Stern, PsyD: Bad parenting, lack of discipline, and lax parenting cannot and do not cause ADD/ADHD.
Most children aren't checked for ADHD until they're school age, but kids as young as4 can be diagnosed, according to guidelines set by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). At that age, many kids are active and impulsive.
When children with these conditions become aggressive, they often do so because they have difficulty dealing with their anxiety or frustration and can't verbalize their feelings as others do. The aggression may also be a form of impulsivity. Impulsivity And then there are the disruptive behavior disorders.
There is no single test that can be used to diagnose attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adults. ADHD is diagnosed after a person has shown some or all of the symptoms of ADHD on a regular basis for more than six months. In addition, symptoms must be present in more than one setting
The Social Learning Theory denies that humans are innately aggressive and that frustration automatically leads to aggression. Instead Bandura (1973) argues that aggression is learned in two basic ways: (1) from observing aggressive models and (2) from receiving and/or expecting payoffs following aggression.
In many cases, a family doctor is the first person to consult with if you suspect that you or your child has ADHD. The best ADHD specialist — whether he or she is a psychiatrist, psychologist, pediatric neurologist, or something else — will have had years of experience in diagnosing and treating ADHD.

